1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> using namespace std ;int sum (vector <int > numbers) if (numbers.empty()) return 0 ; if (numbers.size()==1 ) return 0 ; sort(numbers.begin(),numbers.end()); int sum=0 ; for ( vector <int >::iterator it = numbers.begin()+1 ;it != numbers.end()-1 ;it++) sum += *it; return sum; } int main () vector <int > n; n.push_back(1 ); n.push_back(3 ); n.push_back(5 ); cout << sum(n); return 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 vector <int > a = {1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ,7 };for (int i : a) cout << i;
Sum of positive
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> int hexToDec (std ::string hexString) reverse(hexString.begin(),hexString.end()); int base = 1 ; int sum =0 ; bool fu = 0 ; for (string ::iterator it = hexString.begin() ; it != hexString.end() ; it++ ){ if ( *it == '-' ) {fu = 1 ; continue ;} int num = 0 ; if ( *it >= 'A' && *it <= 'F' ) num = *it - 'A' + 10 ; else if ( *it >= 'a' && *it <= 'f' ) num = *it - 'a' + 10 ; else num = *it - '1' + 1 ; sum += num * base; base *= 16 ; } return fu?-sum:sum; }
1 2 for (string ::iterator it = hexString.begin() ; it != hexString.end() ; it++ )
Hex to Decimal
1 2 3 4 5 #include <string> int hexToDec (const std ::string & hexString) return std ::stoi(hexString, nullptr , 16 ); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 #include <ios> int hexToDec (std ::string hexString) int n; std ::istringstream (hexString) >> std ::hex >> n; return n; }
1 2 3 int hexToDec (std ::string hexString) return (int )strtol(hexString.c_str(), 0 , 16 ); }
1 2 3 4 5 int hexToDec (std ::string hex) int decValue; sscanf (hex.c_str(), "%x" , &decValue); return decValue; }
Vowel Count
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 #include <string> using namespace std ;int getCount (const string & inputStr) int num_vowels = 0 ; vector <char > vowels = {'a' , 'e' , 'i' , 'o' , 'u' }; for (int it = 0 ; it != inputStr.size() ; it++ ) for (char ch : vowels ) if ( ch == inputStr[it] ) num_vowels++; return num_vowels; } for (string ::const_iterator it = inputStr.begin() ; it != inputStr.end() ; it++)
优秀解答:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 int getCount (const string & inputStr) return count_if(inputStr.begin(), inputStr.end(), [](const char ch) { switch (ch) { case 'a' : case'e': case 'i': case 'o': case 'u' : return true ; default : return false ;} }); } #include <string> using namespace std ;bool is_vowel (char c) return (c == 'a' || c == 'e' || c == 'i' || c == 'o' || c == 'u' ); } int getCount (const string & inputStr) return count_if(inputStr.begin(), inputStr.end(), is_vowel); }
Invert values
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 #include <vector> std ::vector <int > invert(std ::vector <int > values){ std ::vector <int > v2; for_each(values.begin(),values.end(),[ &v2](int c){ v2.push_back(-c); }); return v2; }
1 2 3 4 [](int x, int y) { return x + y; } [](int & x) { ++x; } []() { ++global_x; } []{ ++global_x; }
技巧:
没有return , 则 lambda的返回类型是void
如果没有参数,则可以省略参数
1 2 3 4 5 6 [] [x, &y] [&] [=] [&, x] [=, &z]
算法transform()提供以下两种能力:
1.第一形式有4个参数,把源区间的元素转换到目标区间。也就是说,复制和修改元素一气呵成;
transform(sourceBeg,sourceEnd,destBeg,op)
(1)针对源区间[sourceBeg,sourceEnd)中的每一个元素调用:op(elem) 并将结果写到以destBeg起始的目标区间内;
(2)返回目标区间内“最后一个被转换元素”的下一个位置,也就是第一个未被覆盖的元素位置;
(3)调用者必须确保目标区间有足够的空间,要不就得使用插入型迭代器;
(4)sourceBeg于destBeg可以相同,所以,和for_each()算法一样,你可以使用这个算法来变动某一序列内的元素;
(5)如果想以某值替换符合某一准则的元素,应使用replace()算法;
(6)复杂度:线性;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std ;int test () vector <int > coll1; for (int i=1 ;i<9 ;i++) coll1.push_back(i); transform(coll1.begin(),coll1.end(),coll1.begin(),negate<int >()); for (int i=0 ;i<8 ;i++) cout << coll1.at(i) <<endl ; }
2.第二形式有5个参数,将前两个源序列中的元素合并,并将结果写入目标区间。
transform(source1Beg,source1End,source2Beg,destBeg,op)
(1)针对第一源区间[source1Beg,source1End)以及“从source2Beg开始的第二源区间”的对应元素,调用:op(source1Elem,source2Elem) 并将结果写入以destBeg起始的目标区间内;
(2)返回区间内的“最后一个被转换元素”的下一位置,就是第一个未被覆盖的元素的位置;
(3)调用者必须保证第二源区间有足够空间(至少拥有和第一区间相同的空间大小);
(4)调用者必须确保目标区间有足够空间,要不就得使用插入型迭代器;
(5)source1Beg,source2Beg,destBeg可以相同。所以,可以让元素自己和自己结合,然后将结果覆盖至某个序列;
(6)复杂度:线性;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std ;int test () vector <int > coll1; for (int i=1 ;i<9 ;i++) coll1.push_back(i); transform(coll1.begin(),coll1.end(),coll1.begin(),coll1.begin(),multiplies<int >()); for (int i=0 ;i<8 ;i++) cout << coll1.at(i) <<endl ; }
http://lib.csdn.net/article/cplusplus/32641
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include <queue> #include <string> using namespace std ;std ::string removeExclamationMarks (std ::string str) queue <char > st; for (string ::iterator it = str.begin() ; it != str.end() ; it++) if ( *it != '!' ) st.push(*it); string s; for (int i = st.size() ; i >0 ; i--){ s += st.front(); st.pop(); } return s; }
1 2 3 4 5 int maxMultiple (int divisor, int bound) if ( bound % divisor == 0 ) return bound; return divisor * ( bound / divisor); }
部分排序
头文件:#include<algorithm>
作用:nth_element(a+l,a+k,a+r)
它会使a这个数组中区间[l,r)内的第k大的元素处在第k个位置上(相对位置),**但是它并不保证其他元素有序!**且第 n 个元素之前的元素都小于它,但不必是有序的。同样,第 n 个元素后的元素都大于它,但也不必是有序的。
排序后a[n]就是数列中第n+1大的数
1 2 nth_element(intVect.begin(),intVect.begin()+3 ,intVect.end()); cout << intVect[2 ]<< endl ;
https://zhidao.baidu.com/question/1447317576049306340.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 using namespace std ;class Accumul { public : static std ::string accum (const std ::string &s) stringstream result; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) result << "-" << string (1 , toupper (s[i])) << string (i, tolower (s[i])); return result.str().substr(1 ); } }; class Accumul { public : static std ::string accum (const std ::string &s) std ::string result; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { result.append("-" ); result.append(std ::string (1 ,toupper (s[i]))); result.append(std ::string (i,tolower (s[i]))); } return result.substr(1 ,result.length()); } };
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 #include <string> #include <sstream> using namespace std ;string highAndLow (const string & numbers) string single; stringstream ss (numbers) vector <int > s; while ( getline(ss,single,' ' ) ) s.push_back(stoi(single)); sort(s.begin(),s.end(),greater<int >()); stringstream sss; sss << s.at(0 ) << " " << s.at(s.size() - 1 ) ; return sss.str(); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <boost> using namespace std ;using namespace boost;int main () string s = " hello boost!! " ; trim(s); cout << s << endl ; }
std::numeric_limits<int>::max ()1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 #include <vector> #include <algorithm> using namespace std ;int minSum (vector <int >passed) sort(passed.begin(),passed.end()); int sum = 0 ; int n = passed.size(); for (int i=0 ;i< n/2 ; i++){ sum += passed.at(i) * passed.at(n-1 -i); } return sum ; } int main () cout << minSum({5 ,4 ,2 ,3 }); return 0 ; }
函数形参为vec时,可以直接将{x1,x2,x3}当参数传入。
定义在 numeric 头文件中的 inner_product() 算法可以计算两个 vector 的内积。这个函数模板有 4 个参数:前两个参数是定义第 1 个 vector 的输入迭代器,第 3 个参数是确定第 2 个 vector 的开始输入迭代器,第 4 个参数是和的初值。算法会返回 vector 的内积。例如:
cout << inner_product(begin(passed),begin(passed)+n,passed.rbegin(),0) << endl;
关于删除可迭代对象中元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 std ::list < int > List;std ::list < int >::iterator itList;for ( itList = List.begin(); itList != List.end(); ){ if ( WillDelete( *itList) ) itList = List.erase( itList); else itList++; } std ::list < int > List;std ::list < int >::iterator itList;for ( itList = List.begin(); itList != List.end(); itList++){ if ( WillDelete( *itList) ) List.erase( itList); }
错误原因:在调用erase方法之后使用“++”来获取下一个元素的位置,由于在调用erase方法以后,该元素的位置已经被删除,如果在根据这个旧的位置来获取下一个位置,则会出现异常。
在Python里面遍历删除元素时,下标问题,会使略过元素==> 解决方法: if,else
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 # include <string> std ::string disemvowel (std ::string str) for (std ::string ::iterator it = str.begin() ; it != str.end() ;){ if ( *it == 'A' || *it == 'I' || *it == 'U' || *it == 'E' || *it == 'O' || *it == 'a' || *it == 'o' || *it == 'i' || *it == 'u' || *it == 'e' ) str.erase(it); else it++; } return str; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 # include <string> # include <regex> std::string disemvowel(std::string str){ std::regex vowels("[aeiouAEIOU]"); return std::regex_replace(str, vowels, ""); }
string:: string::find(string &);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 int main () string a="abcdefghigklmn" ; string b="def" ; string c="123" ; string ::size_type idx; idx=a.find(b); if (idx == string ::npos ) cout << "not found\n" ; else cout <<"found\n" ; idx=a.find(c); if (idx == string ::npos ) cout << "not found\n" ; else cout <<"found\n" ; return 0 ; }
当没有找到时返回string::npos
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class CountDig {public : static int nbDig (int n, int d) }; using namespace std ;int contain (int num,int d) int n =0 ; while ( num >= 1 ){ int ge = num % 10 ; num = num / 10 ; if ( ge == d) n++; } return n; } int CountDig::nbDig(int n, int d){ vector <int > v; for (int i=0 ; i <= n ; i++) v.push_back( i*i ); int cnt =0 ; for_each(v.begin(),v.end(),[d,&cnt](int x){ int appn = contain(x,d); cnt += appn ; }); return d==0 ?++cnt:cnt ; }
问题尚未解决
isalpha的使用,sum为int类型,当sum+= char类型的c时,实际加的就是c的ASCII码值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 int charvalue (std ::string s) int sum = 0 ; for (char &c : s){ if (!std ::isalpha (c)) return 0 ; sum += std ::toupper (c); } return sum; } bool compare (std ::string s1, std ::string s2) return charvalue(s1) == charvalue(s2); }
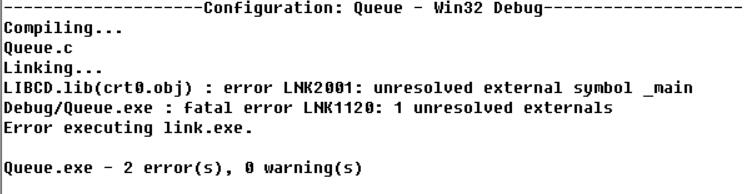
main函数报错
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 #include <stdio.h> #define MAXN 10 typedef float ElementType;ElementType Average ( ElementType S[], int N ) ;int main () ElementType S[MAXN]; int N, i; scanf ("%d" , &N); for ( i=0 ; i<N; i++ ) scanf ("%f" , &S[i]); printf ("%.2f\n" , Average(S, N)); return 0 ; } ElementType Average ( ElementType S[], int N ) { int i; ElementType sum; for (i=0 ;i<N;i++) sum += S[i]; return sum/(ElementType)(N); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> typedef struct Node *PtrToNode ;struct Node { int Data; PtrToNode Next; }; typedef PtrToNode List; int FactorialSum ( List L ) int main () int N, i; List L, p; scanf ("%d" , &N); L = NULL ; for ( i=0 ; i<N; i++ ) { p = (List)malloc (sizeof (struct Node)); scanf ("%d" , &p->Data); p->Next = L; L = p; } printf ("%d\n" , FactorialSum(L)); return 0 ; } int FactorialSum ( List L ) struct Node * p = L ; int sum = 0 ; while ( p ){ int fac=1 ; for (int i=1 ;i<=p->Data ;i++) fac *= i; sum += fac; p = p->Next; } return sum; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> int IsTheNumber ( const int N ) int main () int n1, n2, i, cnt; scanf ("%d %d" , &n1, &n2); cnt = 0 ; for ( i=n1; i<=n2; i++ ) { if ( IsTheNumber(i) ) cnt++; } printf ("cnt = %d\n" , cnt); return 0 ; } int IsTheNumber ( const int N ) int n = (int )sqrt (N); if ( N == n*n ) { int arr[10 ] = {0 }; int m = N; while ( m > 0 ){ int tmp = m%10 ; arr[tmp] += 1 ; for ( int i = 0 ;i<10 ;i++){ if ( arr[i] == 2 )return 1 ; } m /= 10 ; } return 0 ; }else return 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 #include <stdio.h> int Count_Digit ( const int N, const int D ) int main () int N, D; scanf ("%d %d" , &N, &D); printf ("%d\n" , Count_Digit(N, D)); return 0 ; } Count_Digit ( const int N, const int D ){ int cnt =0 ; if ( N == 0 ) return 1 ; int m =N>0 ?N:-N; while (m > 0 ){ int tmp = m%10 ; if ( tmp == D) cnt++; m /= 10 ; } return cnt; }
题解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 void Print_Factorial ( const int N ) long i,s=1 ; if (N>=0 &&N<=12 ){ for (i=2 ;i<=N ;i++)s *= i; printf ("%ld\n" ,s); }else if (N>12 &&N<=1000 ){ int num[3000 ] = {0 }; num[0 ] = 1 ; int k=1 ; int n=0 ; int temp; for (int i=2 ;i<=N ;i++){ for (int j=0 ;j<k;j++){ temp = num[j]*i+n; num[j] = temp%10 ; n = temp/10 ; } while (n!=0 ){ num[k] = n%10 ; n /=10 ; k++; } } for (int x=k-1 ;x>=0 ;x--)printf ("%d" ,num[x]); } else { printf ("%s\n" ,"Invalid input" ); } }
我的做法(错误):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 int mutliply (int a[],int n,int b) for (int i = n - 1 ;i >= 0 ; i--){ int tmp = a[i] * b; while ( tmp >= 10 ) { tmp -=10 ; a[i+1 ] += 1 ; } a[i] = tmp; } } void Print_Factorial ( const int N ) if ( N < 0 ) { printf ("Invalid input" ); return ; } int a[10000 ]={0 }; a[0 ] = 1 ; int n =10000 ; for (int i=1 ;i<=N;i++){ mutliply(a,n,i); } for (int i=n-1 ;i >= 0 ; i--) printf ("%d " ,a[i]); }
总结 :
如果arr[0] = 1, 则得逆序输出。
由于要考虑前缀0的原因,必须考虑位数问题,这也是为什么我的方法一开始没有考虑位数问题,最后就算不下去的原因、
修改后重版
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 void mutliply (int a[],int *n,int b) int w = 0 ; for (int j = 0 ;j < *n; j++){ int tmp = a[j] * b + w; a[j] = tmp %10 ; w = tmp / 10 ; } while ( w != 0 ){ a[ *n ] = w %10 ; w /= 10 ; (*n) ++; } } void Print_Factorial ( const int N ) if ( N < 0 ) { printf ("Invalid input" ); return ; } int a[10000 ]={0 }; a[0 ] = 1 ; int n = 1 ; for (int i=2 ; i <= N;i++){ mutliply(a,&n,i); } for (int i= n-1 ;i >= 0 ; i--) printf ("%d" ,a[i]); }
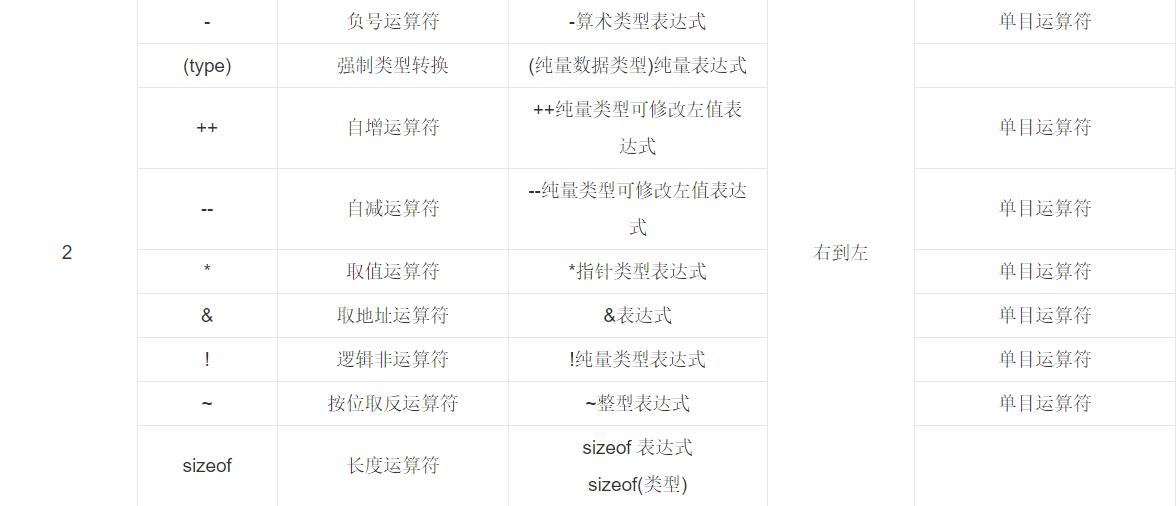
关于++ 和取地址符*的优先级顺序
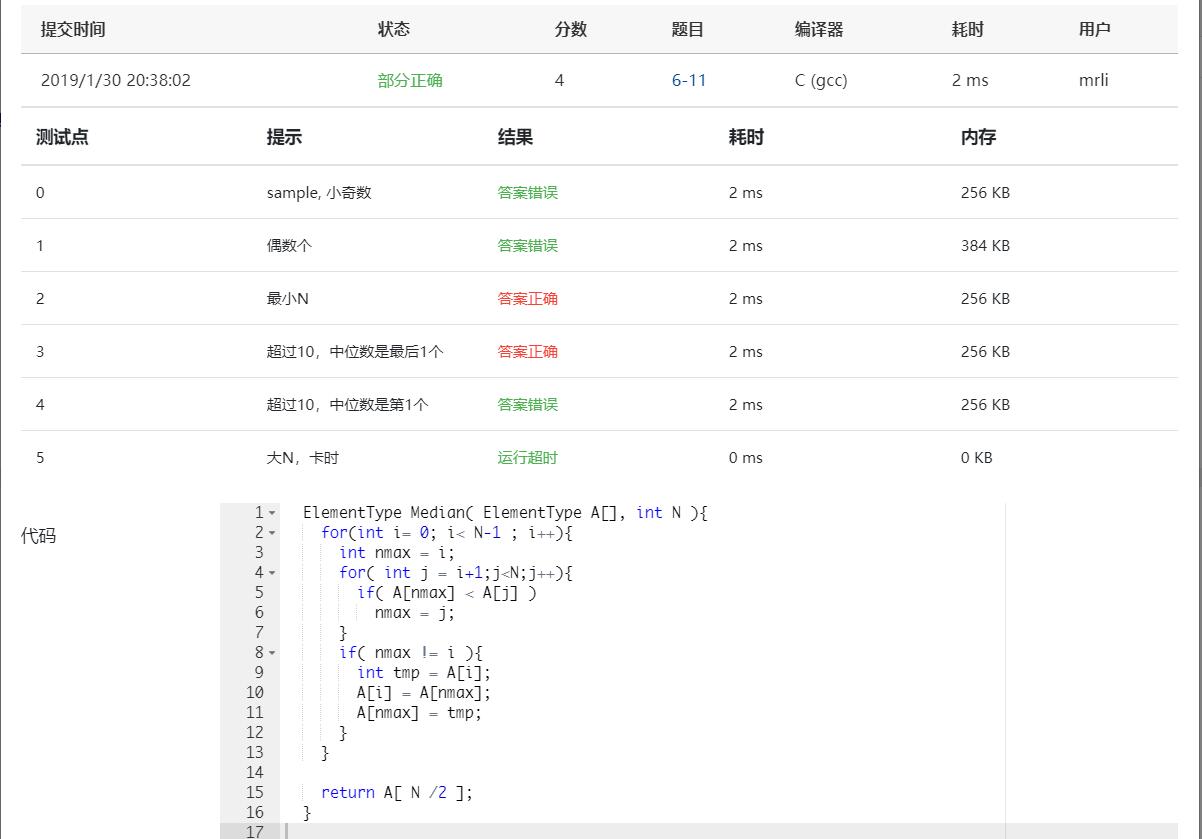
开始用冒泡算法,最后一个测试点过不去
用快速排序,最后一个测试点过不去,数据太多数相同;数据特殊导致时间复杂度退化。
用希尔排序,ac
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 ElementType Median ( ElementType A[], int N ) { for (int i= 0 ; i< N-1 ; i++){ int nmax = i; for ( int j = i+1 ;j<N;j++){ if ( A[nmax] < A[j] ) nmax = j; } if ( nmax != i ){ int tmp = A[i]; A[i] = A[nmax]; A[nmax] = tmp; } } return A[ N /2 ]; }
运行后PE …
搜了题解,发现全部用的是 希尔排序(shell_sort)
希尔排序也是一种插入排序,它是简单插入排序经过改进之后的一个更高效的版本,也称为缩小增量排序
同时该算法是冲破O(n2)的第一批算法之一
关于希尔排序increment(增量)的取法
增量increment的取法有各种方案。最初shell提出取increment=n/2向下取整 ,increment=increment/2向下取整,直到increment=1。但由于直到最后一步,在奇数位置的元素才会与偶数位置的元素进行比较 ,这样使用这个序列的效率会很低。后来Knuth提出取increment=n/3向下取整+1 .还有人提出都取奇数为好,也有人提出increment互质为好。应用不同的序列会使希尔排序算法的性能有很大的差异。
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_37818081/article/details/79202115
题解:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 ElementType Median ( ElementType A[], int N) { int i, j, Increment; ElementType Tmp; for ( Increment = N / 2 ; Increment > 0 ; Increment /= 2 ){ for ( i = Increment; i < N; i++){ Tmp = A[ i ]; for (j = i;j >= Increment ; j -= Increment ){ if ( Tmp < A[ j - Increment ]) A[ j ] = A[ j - Increment ]; else break ; } A[ j ] = Tmp; } } return A[ N / 2 ]; } void shell_sort (ElementType A[],int N) ElementType Median (ElementType A[],int N) { if (N==1 ) return A[0 ]; shell_sort(A,N); return A[N/2 ]; } void shell_sort (ElementType A[],int N) int i,j,gap; for (gap=N/2 ;gap>0 ;gap/=2 ) for (i=gap;i<N;i++) for (j=i-gap; j>=0 && A[j]>A[j+gap] ; j-=gap){ ElementType temp=A[j]; A[j]=A[j+gap]; A[j+gap]=temp; } }
1 2 3 4 int even ( int n ) return n%2 ==0 ; }
题目要求
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <iostream> using namespace std ;#define MAXSIZE 50 typedef int KeyType;typedef struct { KeyType key;} ElemType; typedef struct { ElemType *R; int length; } SSTable; void Create (SSTable &T) int i; T.R=new ElemType[MAXSIZE+1 ]; cin >>T.length; for (i=1 ;i<=T.length;i++) cin >>T.R[i].key; } int Search_Bin (SSTable T, KeyType k) int main () Create(T); cin >>k; int pos=Search_Bin(T,k); if (pos==0 ) cout <<"NOT FOUND" <<endl ; else cout <<pos<<endl ; return 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 int Search_Bin (SSTable T, KeyType k) int low = 1 , high = T.length ; int m; while ( low <= high){ m = (low+high) / 2 ; if ( T.R[m].key == k ) return m ; else if (k< T.R[m].key ) high = m-1 ; else low = m+1 ; } return 0 ; } #include <cstdio> int binsearch (int a[],int N,int k) int low=0 ,high = N -1 ; int m; while ( low<=high){ m = (low +high ) /2 ; if ( a[m] < k) low = m+1 ; else if ( a[m] > k) high = m -1 ; else return m; } return -1 ; } int main () int a[10 ]; int N; scanf ("%d" ,&N); for (int i= 0 ;i<N ;i++) scanf ("%d" ,&a[i]); int k; scanf ("%d" ,&k); int pos = binsearch(a,N,k); if ( pos == -1 ) printf ("NOT FOUND" ); else printf (" index is : %d" ,pos); return 0 ; }
编程题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 #include <cstdio> int main () int N; while ( scanf ("%d" ,&N) == 1 ){ int foot = N / 30.48 ; int inch = 12 * ( N / 30.48 - foot); printf ("%d %d\n" ,foot, inch); } return 0 ; }
题目考察了对提取不同位数,再组合的能力
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 #include <cstdio> int main () int x,y; while ( scanf ("%d%d" ,&x,&y) == 2 ){ int hour_split = x/100 ; int reminderm = y % 60 + x%100 ; int moreh = reminderm / 60 ; int h = hour_split+ y / 60 + moreh; int leftm = reminderm % 60 ; printf ("%d\n" , h * 100 + leftm); } return 0 ; } #include <cstdio> int main () int x,y; int minush = 0 ; int h ; int moreh ; while ( scanf ("%d%d" ,&x,&y) == 2 ){ int hour_split = x/100 ; int reminderm = y % 60 + x%100 ; int leftm = reminderm % 60 ; if ( leftm < 0 ){ moreh = reminderm / 60 - 1 ; int minusm = 60 + leftm ; h = hour_split+ y / 60 + moreh ; printf ("%d\n" , h * 100 + minusm ); }else { moreh = reminderm / 60 ; h = hour_split+ y / 60 + moreh; printf ("%d\n" , h * 100 + leftm ); } } return 0 ; }
题解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 #include <stdio.h> int main () int basis, add; scanf ("%d %d" , &basis, &add); if (add >= 0 ) { int up = (basis % 100 + add) / 60 ; int min = (basis % 100 + add) % 60 ; int end = (basis / 100 ) * 100 + 100 * up + min; printf ("%d" , end); } else { int down = (basis % 100 + add) / 60 ; int dmin = (basis % 100 + add) % 60 ; int end = (basis / 100 ) * 100 + 100 * down - 100 + 60 + dmin; printf ("%d" , end); } return 0 ; }
7-3 逆序的三位数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #include <iostream> using namespace std ;int main () int N; while ( cin >> N ){ int a = N/100 ; int b= N/10 %10 ; int c= N%10 ; if ( c == 0 ){ if ( b==0 ){ cout << a; }else { cout << a + b*10 ; } }else { cout << 100 * c +10 *b + a; } } return 0 ; }
除夕过节
过年休息
字典序比较–>贪心
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 long long Mode (long long a, long long b, long long mode) long long sum = 1 ; a = a % mode; while (b > 0 ) { if (b % 2 == 1 ) sum = (sum * a) % mode; b /= 2 ; a = (a * a) % mode; } return sum; }
当然有时候你可能会碰到用&的运算符的代码实现,其实和这个大致相同,只不过是用&操作符对b的奇偶性进行判断而已
补充:a=2 ,b=0 ,c=1 这种很简单的情况却会WA
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 #include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int a,b,c; int ans=1; while(scanf("%d %d %d",&a,&b,&c)!=EOF){ //int ans = 1; if(b>0){ a=a%c; int h; h=b; while(h>0) { if(h%2==1) ans=(ans*a)%c; h=h/2; a=(a*a)%c; } // if(b==0 && c==1) // cout<<"0"<<endl; cout<<ans<<endl; } else if(b==0 && c==1) cout<<"0"<<endl; else if(b==0 && c!=1) cout<<"1"<<endl; } return 0; }
二进制位中,1 & 1 = 1,其余组合均为0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 long long Mode (long long a, long long b, long long mode) long long sum = 1 ; while (b) { if (b & 1 ) { sum = (sum * a) % mode; b--; } b /= 2 ; a = a * a % mode; } return sum; }
65536
2 16 2^{16} 2 1 6
4 294 967 296
2 32 2^{32} 2 3 2
unsigned int
0~4294967295
int
-2147483648~2147483647 (10位)
unsigned long
0~4294967295
long
-2147483648~2147483647
long long的最大值
9223372036854775807 (19位)
long long的最小值:
-9223372036854775808
unsigned long long的最大值
1844674407370955161
__int64的最大值
9223372036854775807
__int64的最小值:
-9223372036854775808
unsigned __int64的最大值
18446744073709551615
1、栈区(stack) — 由编译器自动分配释放 ,存放函数的参数值,局部变量的值等。其操作方式类似于数据结构中的栈。堆区(heap) — 一般由程序员分配释放, 若程序员不释放,程序结束时可能由OS回收 。注意它与数据结构中的堆是两回事,分配方式倒是类似于链表,呵呵。全局区(静态区)(static) —,全局变量和静态变量的存储是放在一块的,初始化的 全局变量和静态变量在一块区域, 未初始化的全局变量和未初始化的静态变量在相邻的另 一块区域。
4、文字常量区 —常量字符串就 是放在这里的。 程序结束后由系统释放
5、程序代码区—存放函数体的二进制代码。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> using namespace std ;int c[20000 ][20000 ]; int main () int b[1024 *505 ]; int b2[700 *700 ]; char a[4 *518028 ]; int b1[500000 ]; static int c[20000 ][20000 ]; printf ("1" ); };
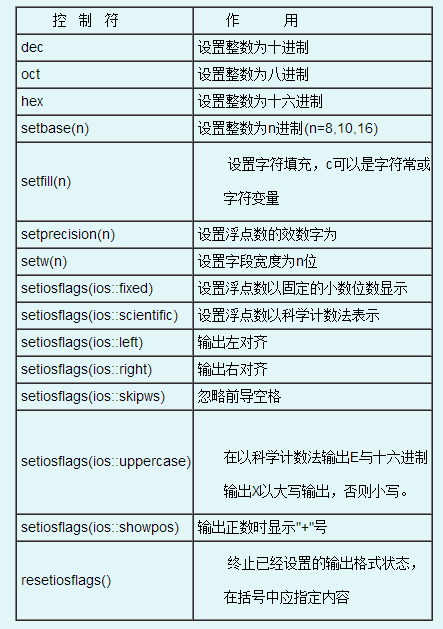
修改C++的输出流, 对小数会进行四舍五入
c++默认的流输出数值有效位是6,包括整数和小数,若数值超出6位,则第七位四舍五入到6位数
fixed :浮点值显示为定点十进制。 默认是小数6位数,不包含整数,若小数位超出6位,则四舍五入到6位数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 #include <iomanip> #include <iostream> using namespace std ;int main () double PI = -3.14125001 ; cout << setprecision(5 ); cout << PI; return 0 ; } int main () double PI = -3.14125001 ; cout << setiosflags(ios::fixed); cout << setprecision(5 ); cout << PI; return 0 ; }
1.setprecision(n)指定一个浮点数的精度默认设置输出的数字的总位数为n,包含整数和小数部分;其中setprecision(0)效果是跟c++默认的流输出数值一样,有效位是6位,包括整数和小数
2.fixed:必须与setprecision(n)配合使用
3.如果与setiosnags(ios::scientific)合用, 可以控制指数表示法的小数位数。setiosflags(ios::scientific)是用指数方式表示实数。
4.resetiosflags(ios::fixed)取消精度的设置。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 #include <iomanip> int main () double PI = 3.51 ; cout << setprecision(1 ); cout << "PI:" << PI; return 0 ; }